Having a well-thought-out recovery policy is crucial for any company to minimise downtime and efficiently resume operations after a disaster.
It typically includes procedures for data backup and recovery, communication protocols, and a detailed chain of command.
In this blog post, we will discuss everything about the disaster recovery policy - it's importance, essential elements, types, benefits and how to develop one.
What is a Disaster Recovery Policy?
In simple words, an IT Disaster Recovery Policy is a plan that details how an organisation responds to unexpected events which can cause business disruption.
It covers scenarios in which critical company systems or information is lost, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or human errors.
Importance of a Disaster Recovery Policy
By having comprehensive Disaster Recovery Policies, business owners can have the peace of mind that their company is prepared for any emergency.
-
It helps to minimise the losses that an organisation may experience due to a disaster.
-
Disaster recovery policies also help to ensure that a business continuity plan is maintained in the event of a disaster.
-
Having a comprehensive disaster recovery policy is also important for ensuring regulatory compliance.
-
A good disaster recovery plan also helps to enhance security by providing detailed guidelines on how data should be backed up and stored securely offsite.
-
Having an effective disaster recovery policy can help improve efficiency by providing clear direction on how employees should respond during an emergency situation.
When developing a disaster recovery policy, it is important to consider two key metrics that play a vital role:
The recovery point objective (RPO): It refers to the amount of time it takes to recover from backup repositories during downtime. These files are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted operations. Determining the minimum backup frequency is one of the key roles of a recovery point objective (RPO).
On the other hand, the recovery time objective (RTO) represents the maximum downtime that an organisation can sustain. During this period, the organisation can restore files from both local and off-site backup repositories to maintain normal operations.
By understanding and incorporating recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO), you can develop a disaster recovery policy that aligns with your specific needs.
Identifying Essential Elements of a Disaster Recovery Policy
Disaster recovery policies are crucial for businesses to mitigate the impact of unexpected events.
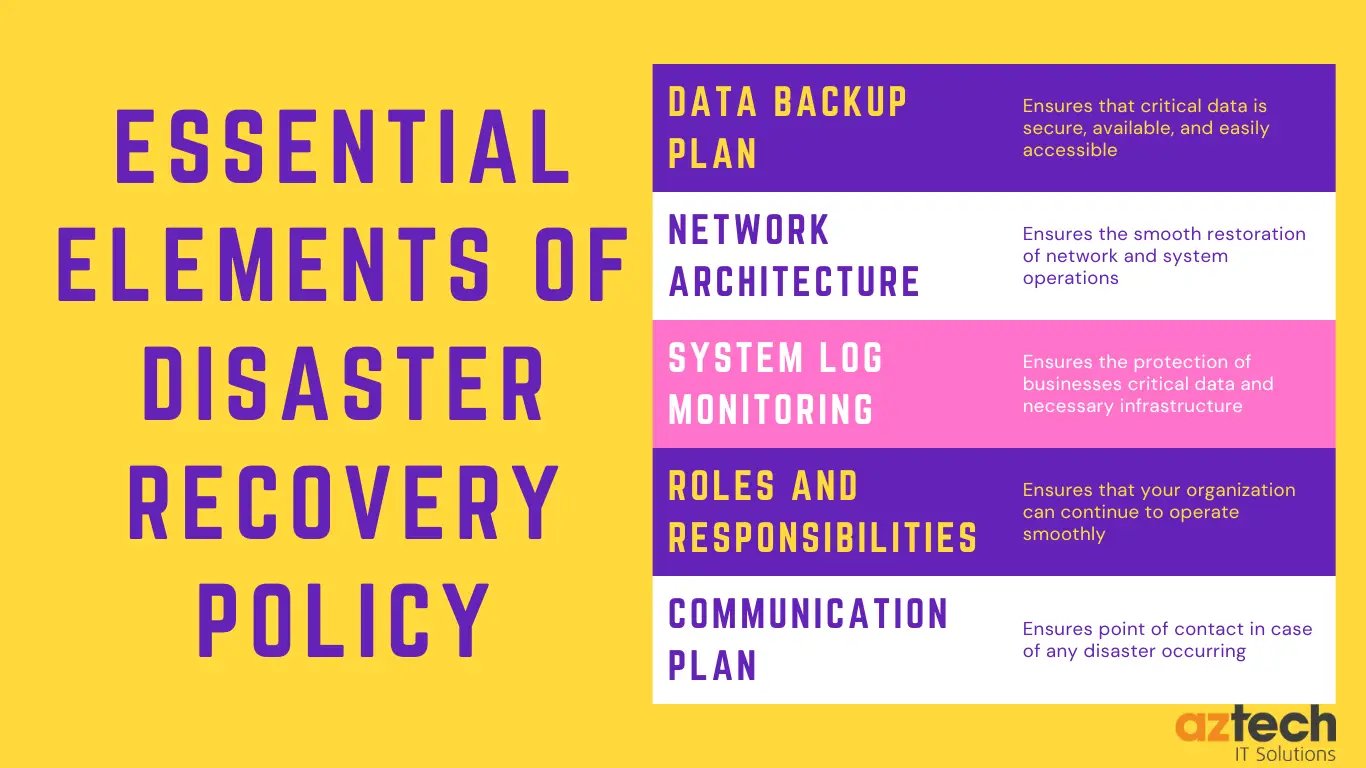
Let's explore some of the key elements that contribute to a successful disaster recovery policy.
Data backup plan
A data backup plan is an effective strategy to ensure that critical data is secure, available, and easily accessible, even when unexpected natural or human-made disasters occur.
Without a data backup plan, businesses can lose critical data, resulting in financial loss, reputation damage, and legal problems.
Good data backup policies not only save you time, but they also instil confidence in your ability to serve customers and maintain business continuity plan in the most challenging times.
Network architecture
Network architecture is among the essential elements of a disaster recovery plan because of its ability to ensure the smooth restoration of network and system operations.
With dependable network architecture, businesses can recover quickly from disasters and avoid massive losses.
A comprehensive should incorporate the most effective network architecture solutions to guarantee a speedy and successful recovery process.
Therefore, every organisation should prioritise network architecture as one of the key aspects of their Disaster Recovery Policy.
System log monitoring
One key component of an effective Disaster Recovery Policy is system log monitoring.
This practice involves continuously and proactively tracking logs for errors, issues, warnings, and anomalies, allowing companies to identify and intervene in potential problems before they escalate into major catastrophes.
By implementing effective system log monitoring protocols, businesses can ensure the protection of their critical data and necessary infrastructure, reducing the risks of significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Designate roles and responsibilities
In times of crisis and uncertainty, a Disaster Recovery Policy is an essential tool to ensure that your organisation can continue to operate smoothly.
While many aspects of disaster recovery plans may require careful consideration, the designation of roles and responsibilities is one of the most crucial elements.
By clearly outlining who is responsible for certain things in the face of a disaster, everyone within the organisation will be able to react quickly and effectively.
This will enable the organisation to minimise damage, ensure the safety of its employees and customers, and even continue operations if possible.
Communication plan
A communication plan is also essential for any successful disaster recovery policy in order to make sure that everyone involved knows what their roles are during an emergency situation and who they need to contact if something goes wrong or help is needed from outside sources like vendors or partners.
The disaster recovery planning process should include contact information for all relevant personnel as well as details about how communications will be handled during an incident and which channels will be used (e-mail, text messages, etc).
What are the different types of Disaster Recovery Policy?
Virtualised Backup Policy
Virtualised backup policies replicate physical servers, workloads, or data into virtual machines hosted in an offsite location, which can be restored in a matter of seconds. This ensures business continuity and reducing system downtime.
With virtualisation, the recovery process is rapid, flexible, and cost-effective. It offers outstanding benefits to businesses of any size, allowing them to protect their data, applications, systems, and users.
Network Backup Policy
Network backup policies outline how a company will respond to emergencies such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures.
Such policies are a critical part of ensuring maximum uptime and minimising data loss, which are both crucial for any business.
With well-crafted policies and a solid disaster recovery plan in place, companies can weather even the most severe network disruptions to keep operations running smoothly and keep customers happy.
Cloud Backup Policy
What happens if disaster strikes your cloud infrastructure? That's where cloud disaster recovery comes in.
By duplicating your data and systems across multiple cloud locations, you can ensure that your business can continue functioning, even if one location goes down.
Whether it's a natural disaster or a cyber attack, having a cloud disaster recovery plan in place can make all the difference.
Data Centre Policy
Disaster recovery plans are essential for any organisation that relies on a data centre to maintain their operations.
These policies ensure that there is a recovery plan in place to minimise disruptions caused by disasters such as power outages, fires, or natural disasters.
Additionally, by implementing a comprehensive data centre policy, organisations can ensure that their data is secure, and their business can continue to function despite any unforeseen circumstances.
Risk Assessment Policy
Risk Assessments include identifying potential threats such as a natural disaster, or human errors that could lead to a disruption in business processes.
Risk assessments also provide organisations with information on what steps can be taken to mitigate these risks and prevent them from occurring in the future.
Testing & Training Policy
Testing & Training are essential components of any Disaster Recovery Policy, as they help ensure that all staff members are knowledgeable about their roles during a disaster recovery process and can effectively respond when needed.
Testing involves running simulations of different scenarios so that staff members can practice responding in a real-life situation.
Training provides staff members with information on their roles during a disaster recovery process, as well as any policies or procedures that need to be followed during this time.
Establishing Best Practices for Your Disaster Recovery Policy
To ensure the success of your disaster recovery policy, consider implementing the following best practices.
These guidelines will help you effectively plan and recover from potential disasters, protecting your data and minimising downtime.
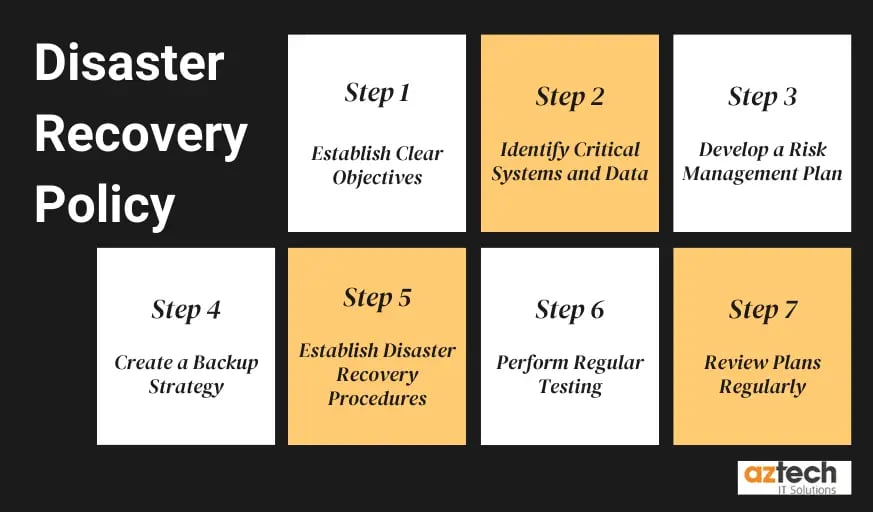
Step 1: Establish Clear Objectives
The first step in establishing a successful disaster recovery policy is to set out clear objectives for the policy. The objectives should be specific, measurable, and achievable, and they should outline what the policy is intended to achieve.
As a disaster recovery policy example, an objective could be “to ensure that all critical systems are restored within 24 hours of a major incident”.
Step 2: Identify Critical Systems and Data
The next step is to identify which systems and data are essential for business operations. This includes any systems or data that would be difficult or impossible to replace quickly in the event of an emergency.
These systems and data should then be prioritised based on their importance to the organisation.
Step 3: Develop a Risk Management Plan
A risk management plan should be developed in order to identify potential threats to the organisation’s critical systems and data, as well as strategies for mitigating those risks.
The plan should also include procedures for responding quickly and effectively in the event of an emergency or disaster situation.
Step 4: Create a Backup Strategy
It is essential that organisations have a reliable backup strategy in place in order to protect their critical systems and data from loss or damage due to disasters or other events outside of their control.
The strategy should include regular backups, offsite storage of backups, automated testing of backups, and other measures designed to ensure that backups can be quickly recovered if needed.
Step 5: Establish Disaster Recovery Procedures
Organisations must also establish procedures for recovering their critical systems and data in the event of an emergency or disaster situation.
These procedures should include detailed instructions on how each system will be recovered, as well as timelines for completing each step of the recovery process.
Step 6: Perform Regular Testing
Regular testing is key to ensuring that disaster recovery planning is effective when it's needed most – during an actual disaster or emergency situation.
Organisations should conduct tests at least once per year (and more frequently if possible) in order to make sure that their plans are up-to-date and can be implemented successfully when needed.
Step 7: Review Plans Regularly
Finally, it is important that organisations review their disaster recovery plans on a regular basis in order to keep them up-to-date with changing technologies and new threats facing the organisation’s critical systems and data.
This review process should involve stakeholders from across the organisation so that any issues can be identified early on before they become major problems down the line.
How do you create a disaster recovery policy?
Here are some important tips to create a disaster recovery policy template for your business.
1. Establish a Business Continuity Team
The first step in creating a disaster recovery policy is to establish a business continuity team.
This team should include representatives from different departments within the organisation, such as IT, finance, and operations.
The team should be responsible for developing the plan and ensuring that it is regularly updated to reflect any changes in the organisation's operations or technology infrastructure.
2. Identify Critical Systems and Data
The next step is to identify which systems and data are critical to the organisation's operations.
This includes any systems or data that must be available in order for the organisation to continue functioning during a disaster event.
Once these systems and data have been identified, it is important to create backups of all critical information so that it can be restored if needed.
3. Develop Procedures for Recovery
Once critical systems and data have been identified, procedures for recovering them should be developed.
These procedures should include steps for restoring systems and data from backups, as well as steps for testing those backups before they are used in production environments.
Additionally, procedures should be established for how employees can access their workstations during a disaster event, such as through remote access or alternate locations if necessary.
What are the benefits of a Disaster Recovery Policy?
Some of the key benefits of implementing a disaster recovery policy for business continuity planning includes:
Improved Business Continuity
A disaster recovery team helps to ensure that a business can continue to operate in the event of a disaster with a business continuity plan.
By having a plan in place, businesses can minimise downtime and ensure that their operations are not disrupted for an extended period of time.
This is especially important for businesses that rely on technology, as even a short period of downtime could result in lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
Reduced Risk of Data Loss
Having a DR Policy also reduces the risk of data loss in the event of a disaster. The policy should include procedures for backing up data regularly, as well as plans for restoring any lost or damaged data.
This ensures that critical information is not lost and that it can be recovered quickly if needed.
Increased Efficiency
Disaster recovery policies also help to improve efficiency by ensuring that processes are documented and standardised across the organisation.
This eliminates confusion when it comes to responding to disasters, as everyone knows exactly what needs to be done and how to do it quickly and efficiently.
Additionally, having standardised processes helps to reduce errors and increase productivity overall.
Improved Security
Having a DR policy also helps to improve security by ensuring that all systems are regularly updated with the latest security patches and software updates.
This reduces the risk of cyber-attacks and other security breaches, which could have disastrous consequences for an organisation's operations and reputation.
Cost Savings
Finally, having a disaster recovery plan can help organisations save money in the long run by reducing downtime due to disasters or system failures, minimising data loss, improving efficiency, and reducing security risks.
In many cases, these cost savings can far outweigh the cost of implementing a Disaster Recovery Policy in the first place.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)






