As the future of work evolves, employers need to be mindful of managing the shifting cybersecurity risks of working from home that come with more employees working from home.
As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, new challenges such as increased cyber threats will arise. Leaving a business exposed to costly data breaches could have serious repercussions for both its reputation and bottom line.
In this blog post, we'll explore the potential cybersecurity risks of working from home in 2024, and what can be done now to protect ourselves against various types of threats posed by remote setups when it comes time for our workforce to transition back home.
We'll also provide cybersecurity prevention methods on how your company can stay secure while working from home while ensuring that your team is productive in their workstations outside the office.
Most Common Cybersecurity Risks of Working from Home
Here are the seven most common cybersecurity risks of working from home in 2024:
1. Unsecured Home Networks
Unsecured home networks are one of the most significant cybersecurity risks of working from home in 2024. As more people work remotely, their home networks could be vulnerable to attackers if they are not properly secured.
To ensure that their home networks are secure, remote workers should always use a strong password and enable encryption on their network.
They should also be aware of any devices that are connected to their network and make sure to keep them up to date with the latest security patches.
2. Vulnerable to Phishing Attacks
Another potential cybersecurity challenge of remote working is phishing attacks, which are attempts by malicious actors to gain access to sensitive information such as passwords or financial information by sending emails that appear to be from legitimate sources.
To protect against these attacks, remote workers should never click on links or open attachments from unknown sources and should always verify the source before providing any personal information.
3. Unencrypted Data Transfers
Unencrypted data transfers can also pose a cybersecurity risk of working from home, as attackers can intercept unencrypted data and potentially gain access to sensitive information.
To mitigate this risk, users should always use secure protocols such as HTTPS or SFTP when transferring data over the internet.
Additionally, they should encrypt any data stored on local devices using an encryption program such as BitLocker or VeraCrypt.
4. Malware Infections
Malware infections are another common cybersecurity challenge of remote working, as attackers may try to install malicious software onto a user’s device to gain access to sensitive information or disrupt operations.
To prevent malware infections, users should ensure that their devices have up-to-date antivirus software installed and scan for viruses regularly.
Additionally, they should avoid downloading files from untrusted sources and be cautious when clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
5. Weak Passwords
Weak passwords can also leave remote workers vulnerable to attack, as attackers may be able to guess easily guessable passwords to gain access to accounts or systems.
To ensure that passwords remain secure, users should create strong passwords that contain at least 8 characters and include a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Additionally, remote workers should avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts and change them regularly to mitigate the cybersecurity risks of working from home.
6. Insufficient Access Controls
Insufficient access controls can also pose a cybersecurity risk when working from home if unauthorised individuals can gain access to systems or accounts without proper authentication procedures being followed first.
To mitigate this risk, organisations should implement robust authentication procedures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) which requires additional verification steps beyond just entering a username and password for an individual’s identity to be confirmed before granting them access.
7. Poorly Configured Systems
Finally, poorly configured systems can leave remote workers vulnerable if security settings have not been properly configured by system administrators, prior to deployment in production environments.
Organisations should ensure that all systems have been properly configured by having system administrators review the settings for each system prior deployment in production environments.
Additionally, organisations should consider implementing automated configuration management tools such as Puppet, Chef, or Ansible which can help reduce human error while configuring systems and hence mitigating cybersecurity risks when working from home.
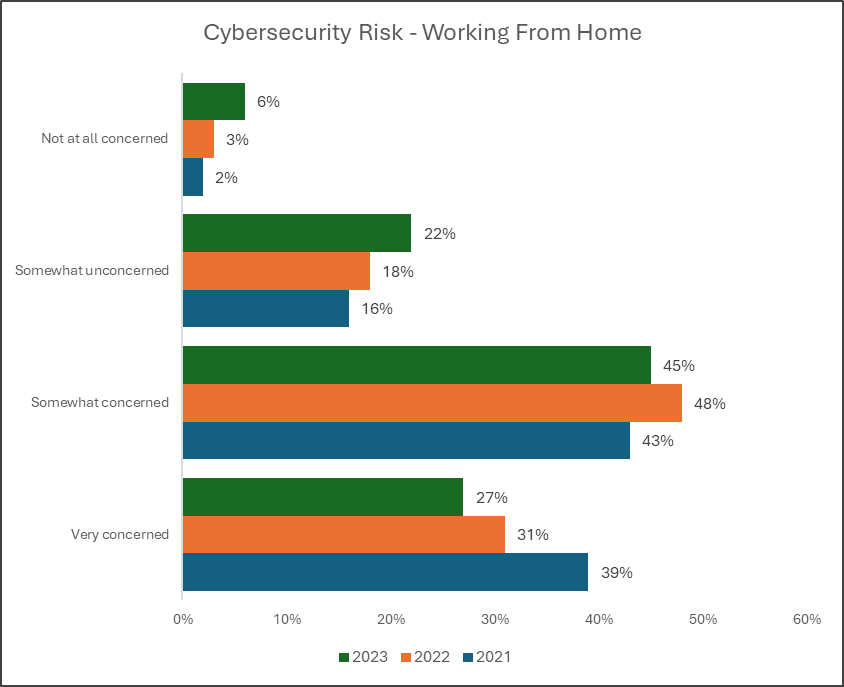
Remote Work Cybersecurity Statistics 2023
According to Statista Research Department, in 2023, the concern regarding cybersecurity risks of working from home employees decreased to 72% globally, compared to almost 80% in 2022.
Interestingly, the number of respondents who expressed no concern about cyber threats related to remote work increased to 6%, doubling from the previous year's 3%.
According to Shred-it, 86% of C-level executives believe that the risk of a data breach is higher when employees work remotely. You can be at a higher risk of losing your property, connecting to unsecured Wi-Fi connections, and unknowingly providing cyber criminals with your data.
A recent study by Upwork stated that 53% of hiring managers agree that companies are embracing more flexible teams as compared to 3 years ago, and according to a survey of SME decision-makers, 80% of UK SMEs have seen a rise in remote working over the past 2 years.
Even now, we all work remotely in some way, such as checking our emails on the go via our phones, quickly finishing off a report on the train, or updating our projects when we get home.
Upwork's report predicts that by 2027, offices will serve as a temporary anchor point, rather than a daily travel destination.
The report goes on to state that almost two-thirds of companies already have employees who work remotely, but more than half (57%) of those companies do not have a remote work policy, and those that do, have not updated it within the past 5 years.
Remote Working Cybersecurity: Essential Best Practices
In today's digital landscape, ensuring cybersecurity while working remotely is of utmost importance.
Implementing the following remote work cybersecurity strategy and best practices can help safeguard sensitive data and protect against potential threats:
1. Use Strong Passwords
When working remotely, it is essential to use strong passwords for all your accounts and devices.
A strong password should contain at least 8 characters and a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
It is also important to avoid using the same password for multiple accounts, as this could put all your data at risk if one account is compromised.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an additional layer of security that requires users to provide two or more pieces of evidence to gain access to an account.
This can include a password, a code sent to a mobile device, or biometric information such as a fingerprint or facial recognition scan.
Enabling MFA on all accounts can help protect against unauthorised access, data breaches and cybersecurity risks of working from home.
3. Protect Your Home Network
It is important to secure your home network when working remotely to protect your data from cybercriminals.
This can be done by ensuring that you have up-to-date antivirus software installed on all devices connected to the network, as well as enabling encryption and firewalls on the router itself.
Additionally, you should change the default username and password on the router for added security.
4. Use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Using a virtual private network (VPN) when accessing sensitive data from outside of the office can help keep your data safe from hackers who may be trying to intercept it over public networks such as Wi-Fi hotspots or cellular networks and hence prevent cybersecurity risks of working from home.
A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and a secure server, allowing you to browse anonymously while keeping your data safe from prying eyes.
5. Secure Your Devices
Securing devices used for remote work is essential to protect confidential information from falling into the wrong hands if they are lost or stolen.
All devices should be locked with a strong passcode or biometric authentication such as facial recognition or fingerprint scanning to prevent unauthorised access if they are lost or stolen.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that all devices are kept up to date with the latest security patches and software updates to protect against potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
6. Be Wary of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are one of the most common methods used by cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers etc.
It is important to be aware of phishing emails and never click on links or download attachments from unknown sources as this could lead to malware being installed on your device or personal information being stolen without your knowledge.
7. Use Encryption Software
Using encryption software when sending sensitive data over email can help protect it from being intercepted by hackers who may be monitoring traffic over public networks such as Wi-Fi hotspots or cellular networks.
Encryption scrambles data so that only those with the correct decryption key can view it, making it much more difficult for criminals to gain access even if they do manage to intercept it while in transit over public networks.
8. Backup Data Regularly
Backing up data regularly can help prevent cybersecurity risks when working from home and minimise any potential losses caused by ransomware attacks which encrypt files until a ransom payment is made.
By backing up files regularly onto external storage media, such as USB drives or cloud storage services like Dropbox, you will always have copies available if needed so that you don't have to pay ransom payments to regain access.
9. Monitor Network Activity
Monitoring network activity can help detect any suspicious activity that may indicate malicious actors attempting to gain unauthorised access and hence prevent cybersecurity risks when working from home.
Keeping track of what applications are connecting outbound, what websites are being visited, and what downloads are taking place can alert you quickly if anything suspicious begins happening so that measures can be taken immediately to stop any potential threats before they become bigger problems.
10. Educate Employees About Cybersecurity Practices
Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices is essential for protecting remote working environments against malicious actors.
Training employees on how to recognise phishing emails and encouraging the use of strong passwords, multi-factor authentication and more, will go a long way in mitigating an organisation’s cybersecurity risks when working from home, for their employees.
By following these remote work cybersecurity best practices, remote workers can create a safer digital environment, mitigating the risk of cybercrime with remote work and maintaining data confidentiality.
How can Aztech help?
Aztech offers User Awareness Training to educate your staff on the warning signs of a potential attack and help them remain vigilant to the latest cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
Additionally, we can assist in updating or putting together your remote work policy - this should be reviewed regularly to ensure it stays up to date with modern technology.
To find out more about Remote Working Cyber Security or just to see how we can help your business improve your IT Security, get in touch today and we’ll be happy to help.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)

-2.png?width=1366&height=768&name=Blog%20Hero%20Banners%20(4)-2.png)
-2.png?width=1366&height=768&name=Blog%20Hero%20Banners%20(5)-2.png)





