In the ever-evolving digital landscape, businesses are constantly looking to maximise efficiency and resource management.
With so many options available, it can be difficult to determine whether you should use private, public, or hybrid clouds.
In this blog post, we'll dive into the difference between a private, public, or hybrid cloud solution and how they can fit within your overall IT strategy.
We'll look at what makes each one unique in terms of security, scalability offerings and pricing models so that you can make an informed decision when evaluating which configuration is best for your business needs.
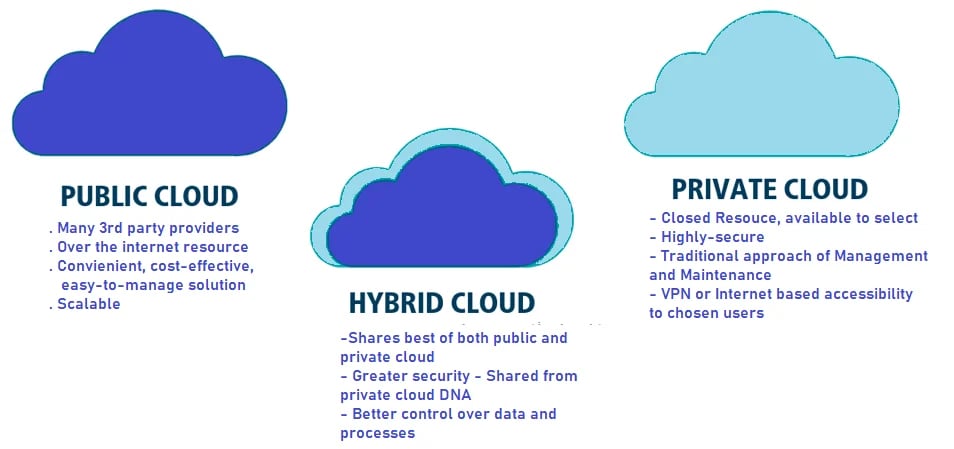
The major difference between public, private and hybrid cloud lies in their accessibility, ownership, and security. Public clouds can be accessed by anyone over the internet, while private clouds are owned by a single organisation and are stored on their own infrastructure. Hybrid clouds, on the other hand, are a combination of both public and private clouds, offering the benefits of both.
Public Cloud: Definition
Public cloud refers to a cloud computing model where cloud services are offered over the internet to the general public.
In simpler terms, the public cloud is a place where businesses can store their data, applications and other services on a shared infrastructure that's managed by a service provider, instead of utilising their own hardware and software.
 Source: Spiceworks
Source: Spiceworks
By choosing the public cloud, businesses can enjoy a range of benefits, including cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and accessibility.
Benefits of Public Cloud
Here are top 5 benefits of public cloud solutions:
1. Cost savings
One of the major benefits of public cloud is cost savings. Public clouds are typically more cost-effective than traditional on-premises solutions, as they allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
This means that businesses can scale up or down depending on their needs without having to invest in expensive hardware or software licenses.
Additionally, public clouds often offer discounts for long-term commitments, allowing businesses to save even more money.
2. Increased agility
Public clouds also provide increased agility compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
With a public cloud, businesses can quickly deploy new applications and services with minimal effort and expense.
This allows them to quickly respond to changing business needs and take advantage of emerging technologies without having to invest in new infrastructure or hire additional personnel.
3. Improved scalability
Public clouds also offer improved scalability compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
With a public cloud, businesses can quickly add or remove resources as needed without having to purchase additional hardware or software licenses.
This allows them to easily adjust their IT environment according to changing business needs and ensures that they always have enough resources available when needed.
4. Enhanced security
Public clouds also provide enhanced security compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
Public cloud providers use advanced security measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication that protect data from unauthorised access and ensure that only authorised users can access sensitive information.
Additionally, public cloud providers regularly update their systems with the latest cybersecurity patches, ensuring that customer data is always protected against the latest threats.
5. Reduced maintenance
Finally, public clouds also reduce maintenance costs compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
Public cloud providers handle all aspects of system maintenance, including server patching, software updates, and hardware repairs, freeing up IT staff from performing these tasks themselves and allowing them to focus on other important tasks instead.
Limitations of Public Cloud
Here are the four major limitations of public cloud solutions:
1. Security
One of the major limitations of public cloud computing is security. When data is stored in the cloud, it can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks, as it is accessible from anywhere in the world.
Additionally, since cloud providers do not have control over who accesses their servers, malicious actors may be able to gain access to sensitive data.
To mitigate this risk, organisations should ensure that they are utilising strong authentication methods and encrypting their data before storing it in the cloud.
2. Compliance
Another limitation of public cloud computing is compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Businesses must ensure that they are compliant with all applicable laws and regulations when storing data in the cloud.
This can include ensuring that personal data is protected according to GDPR guidelines, or that financial information is stored according to PCI DSS standards.
Failing to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines or other penalties for organisations.
3. Availability
Public cloud services can also experience downtime due to a variety of factors such as network outages or server failures.
This can lead to lost productivity and revenue for organisations that rely on these services for their operations.
Additionally, businesses may not have control over when these outages occur, making them difficult to plan around or mitigate against in advance.
4. Cost
The cost of public cloud services can also be a limitation for some businesses as they may not have the budget required to utilise them effectively.
As public clouds become more popular, competition among vendors has increased which has led to lower prices but there are still many services that require significant upfront investments before they can be used effectively by an organisation.
Additionally, organisations must also factor in costs associated with migrating existing applications and workloads into the cloud environment as well as ongoing maintenance costs associated with running them once they are deployed.
Examples of Public Cloud
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a public cloud computing platform that offers a wide variety of services for businesses, including compute, storage, networking, database, analytics, application services, and more.
AWS is one of the most popular public cloud providers and is used by many large companies such as Netflix and Airbnb.
With AWS, users can quickly deploy their applications with minimal effort and cost.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is another popular public cloud provider that provides a wide range of services for businesses.
Azure offers solutions for compute, storage, networking, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and more.
It also offers features such as serverless computing and container orchestration to help users quickly deploy their applications in the cloud.
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a public cloud provider from Google that offers a comprehensive suite of services for businesses.
GCP provides solutions for compute, storage, networking, databases, machine learning (ML), analytics, AI, IoT and more.
It also has features such as serverless computing and container orchestration to help users quickly deploy their applications in the cloud.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud is a public cloud provider from IBM that provides a wide range of services for businesses including compute, storage, networking, databases & analytics & AI & IoT solutions & more.
It also has features such as serverless computing & container orchestration to help users quickly deploy their applications in the cloud.
IBM Cloud also offers hybrid cloud options so that customers can take advantage of both on-premises infrastructure and public cloud resources when needed.
Private Cloud: Definition
Private cloud refers to a type of cloud computing that is solely dedicated to a single organisation.
Unlike public clouds that are available to the general public, private clouds are operated within an organisation's own data centre or hosted by a third-party service provider.
The private cloud provides flexibility, scalability, and greater control to businesses and organisations that require a customised computing environment to meet their specific needs.
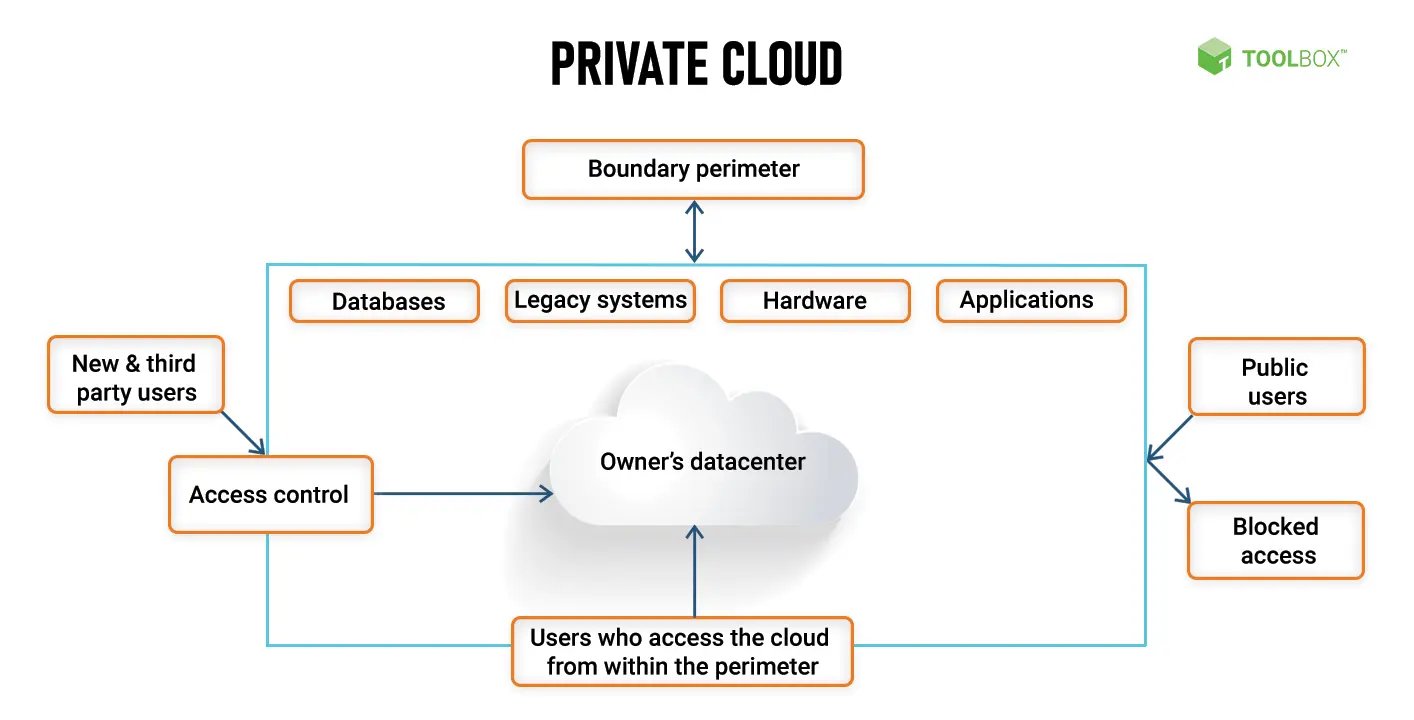
It offers increased security and better regulatory compliance as organisations can implement specific security protocols that are tailored to their unique requirements.
Simply put, private cloud provides a highly secure, scalable, and advanced computing infrastructure that allows businesses to boost their operational efficiency and drive growth.
Benefits of Private Cloud
Here are the top 5 benefits of private cloud for businesses:
1. Improved Security
One of the biggest benefits of a private cloud is improved security. Private clouds enable organisations to store their data in a secure, isolated environment that is not accessible to the public.
This ensures that sensitive data remains safe from cyberattacks and other malicious activities.
Additionally, private clouds can be configured with various security measures such as encryption, two-factor authentication, and access control lists to further protect data.
2. Enhanced Flexibility
Private clouds also offer enhanced flexibility when it comes to scaling up or down computing resources.
With a private cloud, businesses can easily adjust the amount of storage space, processing power, and memory they need without having to purchase additional hardware or software.
This allows them to quickly respond to changing business needs and ensure that they are always running at peak efficiency.
3. Lower Costs
Private clouds can also help reduce costs for organisations by eliminating the need for physical hardware such as servers and networking equipment.
Instead, organisations can use virtualised resources on a private cloud which are much more cost-effective than purchasing and maintaining physical hardware.
Additionally, private clouds allow businesses to pay only for the resources they use, which helps them save money in the long run.
4. Improved Performance
Private clouds also offer improved performance since all of an organisation's resources are stored in one place on a single system instead of multiple systems spread out across different locations or networks.
This makes it easier for applications and services to access data quickly and efficiently without experiencing any delays due to latency issues or network congestion.
Additionally, private clouds enable businesses to take advantage of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) which can further improve performance and productivity levels within business.
5. Greater Control
Organisations also have greater control over their data when using a private cloud since all resources are hosted on their own servers instead of third-party providers’ servers like with public cloud solutions such as Amazon Web Services (AWS).
This gives them full control over who has access to their data and how it is used or shared with external parties such as vendors or partners.
Limitations of Private Cloud
Here are the four limitations of private cloud for businesses:
1. Security
One of the major limitations of private cloud is security. Private clouds are inherently less secure than public clouds due to their reliance on a single provider for all security measures.
As such, they are more vulnerable to malicious attacks, data breaches, and other security threats.
Additionally, private clouds can be difficult to keep up to date with the latest security patches and updates, which can leave them open to attack.
2. Cost
Another limitation of private cloud is cost. Private clouds require significant upfront investments in hardware and software, as well as ongoing maintenance costs for upkeep and support.
These costs can quickly add up over time, making it difficult for businesses to stay within budget when using a private cloud solution.
3. Scalability
Private clouds are also limited in terms of scalability compared to public clouds.
With a public cloud, businesses can easily scale up or down depending on their needs, but with a private cloud this is often not possible due to the hardware and software requirements needed to maintain the system.
This can make it difficult for businesses that experience sudden spikes in demand or need additional resources at short notice.
4. Flexibility
Private clouds also lack flexibility compared to public clouds due to their reliance on a single provider for all services and features.
This means that businesses are limited in terms of what services they can use and how they can customise them for their specific needs, as most providers only offer pre-defined packages that cannot be altered further than what is offered by default.
Examples of Private Cloud
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is one of the most common types of private cloud services. IaaS allows businesses to outsource their hardware needs, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, to a third-party provider.
This allows companies to reduce their capital expenditures and simplify their IT infrastructure. They can then focus on developing and running applications rather than managing hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is another type of private cloud service that provides an entire computing platform to organisations, including both hardware and software components.
PaaS allows companies to quickly develop and deploy applications without having to manage any underlying infrastructure or software components.
It also offers scalability so that organisations can easily increase or decrease their computing resources depending on demand.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is another type of private cloud service that provides access to software applications over the internet.
SaaS eliminates the need for organisations to install and maintain software on their own systems, allowing them to focus on using the applications rather than managing them.
Additionally, SaaS offers scalability so that companies can quickly increase or decrease their usage of an application depending on demand.
Database as a Service (DBaaS)
Database as a Service (DBaaS) is another type of private cloud service that provides access to databases over the internet.
DBaaS eliminates the need for organisations to install and maintain databases on their own systems, allowing them to focus on using the data rather than managing it.
Additionally, DBaaS offers scalability so that companies can quickly increase or decrease their usage of a database depending on demand.
Hybrid Cloud: Definition
Hybrid cloud is an innovative solution in which businesses can run their applications on a combination of both public and private clouds.
Hybrid cloud is better than public and private cloud as by using hybrid cloud, businesses can tap into the flexibility and scalability of public cloud resources while also maintaining the control and security of their own private cloud.
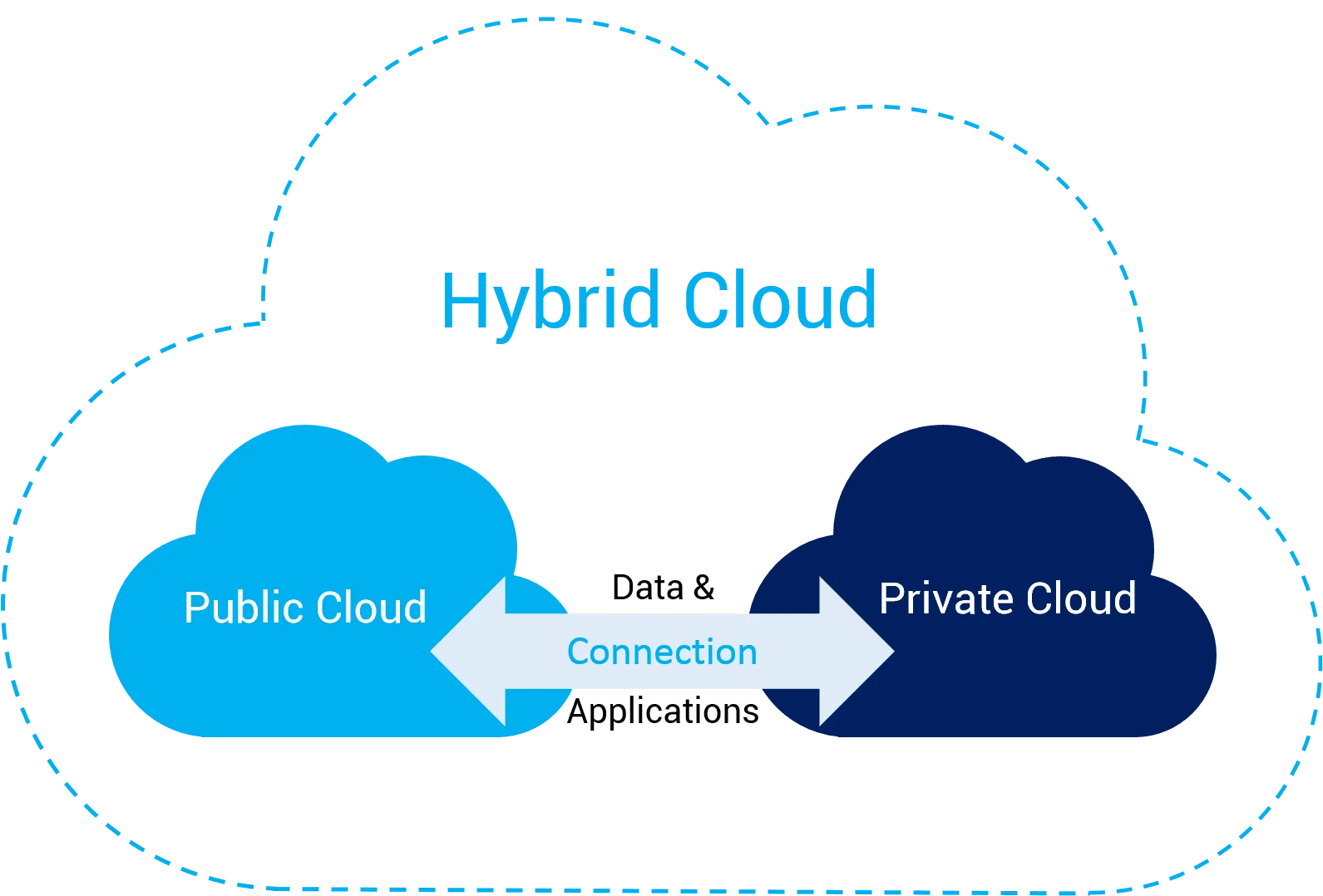
Hybrid cloud also enables organisations to manage their workloads more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Benefits of hybrid cloud
Here are the 5 top benefits of hybrid cloud for businesses:
1. Cost Savings
One of the major benefits of a hybrid cloud is cost savings. By utilising both private and public cloud services, businesses can reduce their overall IT costs by leveraging the economies of scale associated with public cloud offerings and the flexibility and control that comes with a private cloud environment.
Additionally, by using a hybrid cloud model, organisations can avoid large upfront investments in hardware and software since they can purchase only what they need from the public cloud provider.
2. Increased Flexibility
A hybrid cloud also provides increased flexibility for organisations as it allows them to quickly scale their computing resources up or down depending on demand.
This can be particularly beneficial for businesses that experience seasonal fluctuations in demand or those that are dealing with unpredictable workloads.
Additionally, a hybrid cloud allows organisations to easily move workloads between different types of clouds to take advantage of new features or lower costs.
3. Improved Security
Organisations can also benefit from improved security when using a hybrid cloud model.
By utilising both private and public clouds, organisations can better protect their data while still taking advantage of the scalability and cost savings associated with public clouds.
Additionally, by having multiple layers of security across different types of clouds, organisations can ensure that their data is protected against intrusions or malicious actors.
4. High Availability
A hybrid cloud also provides high availability for applications and services as it allows organisations to spread out their workloads across multiple locations in order to reduce downtime due to local outages or disasters such as fires or floods.
Additionally, by leveraging multiple providers, organisations can ensure that their applications are always available even if one provider experiences an outage or other issue.
5. Easier Disaster Recovery
By utilising both private and public clouds, organisations can more easily implement disaster recovery plans as they have access to both on-premise resources as well as off-site backup solutions provided by public cloud vendors such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
This ensures that critical applications and services remain available even in the event of an emergency situation such as a natural disaster or cyber-attack.
Limitations of Hybrid Cloud
Here are the four limitations of hybrid cloud:
1. Security Concerns
One of the major limitations of hybrid cloud is security concerns. Hybrid clouds are composed of both public and private cloud components, which means that data stored in the public cloud is vulnerable to attack from outside sources.
Additionally, many organisations lack the resources to adequately secure their hybrid clouds, leaving them open to potential security breaches.
To ensure that data stored in a hybrid cloud is secure, organisations must invest in robust security measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
2. Complexity
Another limitation of hybrid cloud is complexity. Managing a hybrid cloud can be complicated due to its combination of on-premise and off-premise components.
Businesses must be able to effectively manage multiple vendors, technologies, and environments in order to ensure that their hybrid cloud is functioning properly.
Additionally, businesses must ensure that their on-premise and off-premise components are compatible with one another in order to avoid any potential issues.
3. Cost
The cost of maintaining a hybrid cloud can be prohibitive for some organisations due to the need for additional hardware and software investments as well as ongoing maintenance costs associated with managing multiple vendors and technologies.
Additionally, organisations may need to hire additional staff members with specialised skillsets in order to properly manage their hybrid clouds, which can further increase costs associated with the technology.
4. Vendor Lock-in
Some vendors may require an organisation to use specific hardware or software solutions in order for their hybrid cloud solution to work correctly, which can lead to vendor lock-in situations where business becomes dependent on a single vendor’s products or services.
This can limit an organisation’s ability to switch vendors if they are unhappy with the service they are receiving or if they find a better option elsewhere due to the cost associated with migrating data from one vendor’s platform to another’s platform.
Examples of Hybrid Cloud
Public-Private Cloud
Public-private cloud is a type of hybrid cloud that combines public cloud services with private cloud services.
The public cloud portion of the hybrid is used for less sensitive applications, while the private cloud portion is used for more sensitive applications.
This type of hybrid cloud provides organisations with the ability to take advantage of the scalability and cost savings associated with public clouds, while still ensuring that their data remains secure in a private environment.
Private Cloud Bursting
Private cloud bursting is another type of hybrid cloud that combines on-premises computing resources with public cloud services.
This type of hybrid allows organisations to take advantage of their existing infrastructure and scale up into the public cloud as needed.
This can be beneficial for businesses that experience periods of high demand or need additional capacity during peak times.
Multi-Cloud Model
The multi-cloud model is a type of hybrid cloud that uses multiple public clouds from different vendors in order to provide redundancy and increased availability.
This type of hybrid allows organisations to take advantage of different features offered by each vendor, while also ensuring that their data is spread across multiple providers for added security and reliability.
Hybrid Cloud Storage
Hybrid cloud storage combines local storage with offsite storage solutions such as SaaS (Software as a Service) or IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
This type of hybrid provides organisations with the ability to store data locally for quick access, while also taking advantage of the scalability and cost savings associated with offsite storage solutions.
Additionally, this type of hybrid allows businesses to maintain control over their data since it remains within their own environment even when stored offsite.
Difference Between Private, Public and Hybrid Cloud
Here are the 5 major difference between private, public and hybrid cloud:
| Private | Public | Hybrid | |
| Deployment Model | Hosted in a company’s own data centre or on dedicated hardware that is owned by the company | Hosted in a shared environment such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. | Combines both private and public cloud models for maximum flexibility |
| Security | Offer the highest level of security since they are hosted in a company’s own data centre or on dedicated hardware that is owned by the company | Have less control over their security since they are shared environments, but they still offer strong security measures such as encryption and access control | Combines both private and public cloud models to provide the best of both worlds in terms of security |
| Pricing | More expensive due to the need for dedicated hardware and staff to maintain | Cheaper since they leverage economies of scale from sharing resources across multiple customers | Offers a balance between cost and performance depending on how much of each type of cloud is used |
| Scalability | Limited in terms of scalability due to their reliance on dedicated hardware | Easily scalable due to the shared nature | Highly scalable since it can leverage both private and public cloud resources depending on what is needed at any given time |
| Flexibility | Tends to be more rigid due to their reliance on dedicated hardware | Offers greater flexibility since they leverage economies of scale from sharing resources across multiple customers | Provides maximum flexibility since they combine both private and public cloud models |
1. Deployment Model
The primary difference between private, public, and hybrid clouds is the deployment model.
Private clouds are hosted in a company’s own data centre or on dedicated hardware that is owned by the company.
Public clouds are hosted in a shared environment such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Hybrid clouds combine both private and public cloud models for maximum flexibility.
2. Security
Another major difference between private, public, and hybrid clouds is security.
Private clouds offer the highest level of security since they are hosted in a company’s own data centre or on dedicated hardware that is owned by the company.
Public clouds have less control over their security since they are shared environments, but they still offer strong security measures such as encryption and access control.
Hybrid clouds combine both private and public cloud models to provide the best of both worlds in terms of security.
3. Pricing
The cost of using private, public, and hybrid clouds can also vary greatly depending on the type of cloud being used.
Private clouds tend to be more expensive due to the need for dedicated hardware and staff to maintain it, while public clouds are typically cheaper since they leverage economies of scale from sharing resources across multiple customers.
Hybrid clouds can offer a balance between cost and performance depending on how much of each type of cloud is used.
4. Scalability
Scalability is another major difference between private, public, and hybrid clouds.
Private clouds are generally limited in terms of scalability due to their reliance on dedicated hardware, while public clouds can scale easily due to their shared nature.
Hybrid clouds can offer the best of both worlds in terms of scalability since they can leverage both private and public cloud resources depending on what is needed at any given time.
5. Flexibility
Finally, flexibility is another key difference between private, public, and hybrid clouds when it comes to meeting an organisation’s needs for computing power or storage capacity at any given time.
Private cloud solutions tend to be more rigid due to their reliance on dedicated hardware, while public cloud solutions offer greater flexibility since they leverage economies of scale from sharing resources across multiple customers.
Hybrid cloud solutions provide maximum flexibility since they combine both private and public cloud models, allowing organisations to adjust their usage levels as needed.

-1.png?width=552&height=678&name=text-image%20module%20desktop%20(4)-1.png)


.png?width=2000&name=Case%20study%20(21).png)


-2.png?width=422&height=591&name=text%20image%20tablet%20(31)-2.png)