In 2025, email has become increasingly crucial to business success, and organisations must adhere to a more robust set of email security best practices.
In 2023, the Internet Crime Complaint Centre (IC3) received 21,489 complaints related to the Business Email Compromise (BEC) with adjusted losses of over 2.9 billion, as reported in the Internet Crime Report.
Therefore, employees should implement effective email security best practices to protect sensitive information, prevent unauthorised access, and maintain the integrity of email communications.
In this blog post, we'll explore the best practices for email security in 2025 to reduce cyber risks and stay secure.
Key Highlights:
|
9 Essential Email Security Best Practices for Employees 1. Training on Email Security Best Practices 2. Effective Password Management 3. Use Two-Factor Authentication 4. Stay Vigilant to Phishing Attacks 5. Encrypt Email, Communications, and Attachments 6. Avoid Using Public Wi-Fi 7. Deploy a Gateway Email Content Filter 8. Use Email Security Protocols 9. Use Email Security Tools |
What is Email Security?
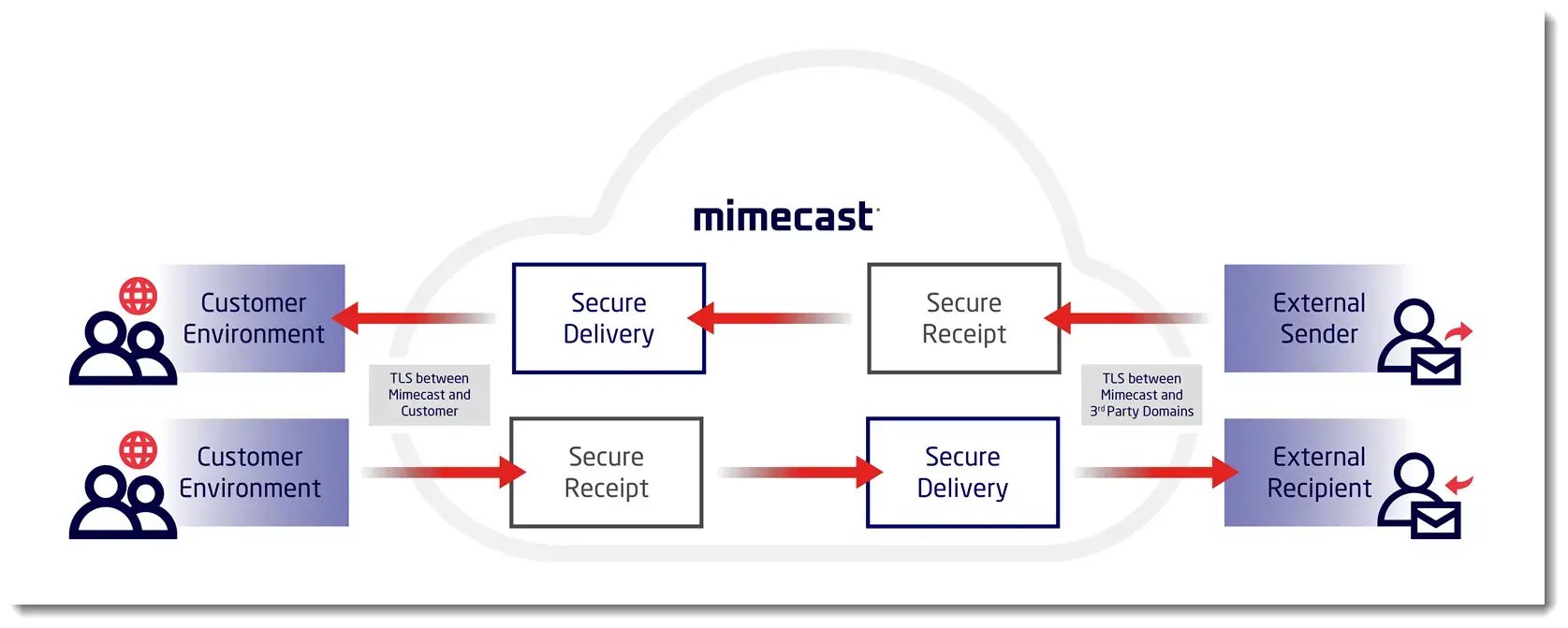 Source: Mimecast
Source: MimecastEmail security is the practice of implementing measures and strategies to safeguard email communication from unauthorised access, threats, and attacks.
This includes using tools, protocols, and best practices to ensure that email systems are protected from threats such as data exfiltration, phishing attacks, spam, malware, impersonation, and other cyber threats.
The key components include email encryption, email security protocols, and secure email gateways that monitor and filter email traffic.
Why is Email Security Important?
Email security is essential because it protects sensitive information, prevents data breaches, and safeguards businesses and personal assets from cyber threats like phishing scams, data exfiltration, malware, and impersonation.
In 2024, the average employee is bombarded with a staggering 121 emails every day, as reported by Venngage.
The numbers show that an astounding 376 billion emails are expected to be sent and received daily worldwide by 2026, highlighting the extensive use of email.
Most businesses rely heavily on email for day-to-day communication. Without proper security measures, emails can easily be intercepted, exposing confidential information such as financial data, personal details, and business strategies.
Email is a central target for cyber criminals aiming to steal personal and financial data, disrupt business operations, or launch broader cyberattacks.
Weak security practices around email can lead to:
-
Data breaches: This is when sensitive information like login credentials, personal details, and company secrets are exposed.
-
Business email compromise (BEC): In this type of attack, hackers take control of a company email account to carry out fraudulent activities.
-
Phishing attacks involve attackers tricking users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious code.
-
Brute force attacks: Hackers use this method to try to gain access to your email account by guessing weak passwords.
| Read More: What is Email Overload and How to Manage it |
Top 9 Best Practices for Email Security

Here are the 9 essential email security best practices for employees:
1. Train Employees on Email Security Best Practices
The first line of defence in email security is security awareness training. Businesses should educate employees about common phishing attacks, suspicious links, and malicious emails, which can reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks.
Training your employees is one of the most critical steps in protecting your business from email threats. Even the most advanced email security tools can be undermined if your employees fall for common scams like phishing or open malicious attachments.
Since human error accounts for a proportion of significant security risks and breaches, building a culture of security awareness is key to reducing risks.
How to effectively train your employees
-
Conduct regular email security awareness training sessions: Businesses should develop training as an ongoing process rather than a one-time event. This can include workshops, online courses, or informational emails detailing the latest email security threats and how to avoid them.
-
Teach employees to recognise phishing emails & spam emails: Phishing emails often contain signs like misspelt words, sceptical links, or an urgent request for personal information. Therefore, employees should learn to spot these red flags and know how to handle such emails (e.g., forwarding them to the IT department for further investigation).
-
Encourage employees to report suspicious emails: Businesses should promote an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting anything unusual, even if they are unsure. In addition, quick reporting can help prevent a small mistake from turning into a larger security breach.
By regularly educating your workforce, you equip them with the knowledge to protect both themselves and the organisation from email-related attacks.
2. Effective Password Management
Passwords are a foundational aspect of email security best practices, yet poor password management practices are one of the most common reasons for breaches.
Businesses should ensure that employees manage their passwords effectively, as this can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorised access.
Create Strong Passwords
A strong password is the first line of defence against cyber-attacks. Instead of simple, easy-to-guess passwords like "password123" or "companyname2024", you should opt for more complex combinations.
Also, you should include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Additionally, you should use passphrases, such as “B@ckyardSunfl0wers2023!”, which are easier to remember but difficult to crack.
Don’t Reuse Passwords Across Accounts
Many users often make the mistake of reusing passwords across multiple accounts and platforms. However, if one account is compromised, others will also be at risk. It is essential to ensure that each account, particularly email, has a unique password.
Businesses should encourage their employees to store and generate strong, unique passwords using a password manager.
Moreover, reusing passwords increases vulnerability, especially if one service experiences a data breach.
Consider Changing Passwords Regularly
There’s been debate about how frequently passwords should be changed. In the past, it was common advice to change passwords every 90 days.
However, frequent password changes can lead to weaker passwords as users tend to create easily memorable patterns.
Instead of regular changes, you should focus on using strong, complex passwords and enable two-factor authentication. You should only change a password when there’s a security concern or suspected breach.
3. Utilise Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) offer an additional layer of security beyond just a password.
In addition to your password, you’ll need to verify your identity using a secondary method, such as a code sent to your mobile phone or an authentication app.
This can prevent hackers from accessing your email, even if they manage to steal your password.
Why is this crucial
Even if a hacker gains access to an employee’s password, they won’t be able to log in without the second authentication factor.
2FA significantly reduces the chances of unauthorised access, as attackers must bypass both the password and the second authentication method.
Businesses should encourage the use of 2FA on all online accounts, that support it, especially for business-related email systems.
4. Stay Vigilant to Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks remain one of the most common and dangerous forms of cybercrime. It involves tricking email recipients into providing sensitive information by pretending to be a legitimate source.
A successful phishing attack can result in serious security breaches, including data theft and financial loss.
Be Wary of Email Attachments
Attachments can hide malicious software, such as viruses, trojans, or ransomware. Before downloading or opening any attachments, you should verify the sender’s identity.
You must confirm with the sender directly if an attachment seems unexpected or suspicious. Also, you should use email spam filtering tools to scan attachments for malware.
Think Before You Click
Many phishing emails include links to malicious websites. These links might look legitimate but could direct you to a site to steal login credentials or install malware.
You should hover over links to see where they lead before clicking. If the email asks you to reset a password or update information, visit the site directly by typing the URL into your browser rather than clicking the link.
Only Access Business Emails on Approved Devices
The best email security practices don’t stop at passwords or software. Devices used to access email systems should also be secure.
Businesses should ensure that employees only access corporate emails on secure email gateway and company-approved devices with the latest security updates.
Additionally, organisations should regularly update antivirus software and ensure all security patches are installed. Also, employees should avoid using unsecured devices or networks, which can compromise email accounts.
| Read More: Phishing-Related Frequently Asked Questions |
5. Encrypt Email, Attachments and Communications
Encryption is a critical tool to protect sensitive data transmitted through emails. Email encryption is critical for protecting financial information, login credentials, and other sensitive data in transit.
When email messages are encrypted, the content becomes unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key, ensuring that even if the email is intercepted, the information remains secure.
Many email providers offer built-in encryption, but it’s also advisable to use third-party encryption tools to protect susceptible communications.
How to implement encryption
-
Use end-to-end encryption to ensure that only the sender and the recipient can read the email.
-
Encrypt sensitive email attachments, such as financial statements or contracts.
-
Ensure your email platform supports encryption protocols, like TLS (Transport Layer Security).
6. Avoid Using Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks are vulnerable to hackers due to a lack of encryption and security measures. Using email over public Wi-Fi exposes your information to attackers who can intercept email traffic or hijack accounts.
Tips for using Wi-Fi securely
-
You should avoid accessing work emails over public Wi-Fi unless necessary.
-
If you are using public Wi-Fi, always connect through a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to add an extra layer of encryption.
-
You should disable file sharing and other unnecessary services when connected to a public network.
7. Deploy a Gateway Email Content Filter
A secure email gateway filter acts as a barrier between your organisation and potential email threats. It scans all incoming and outgoing emails for spam, viruses, and malware, blocking harmful messages before they can reach users.
Benefits of email content filters
-
Automatically detects and filters out suspicious or malicious emails.
-
Reduces the risk of phishing scams, malware, and other email-based attacks.
-
Can be customised to meet the specific needs of your organisation.
8. Use Email Security Protocols
Email security protocols provide an extra layer of defence for secure email communications. Protocols like S/MIME and TLS ensure that emails are transmitted securely and protect them from tampering or unauthorised access.
Key email security protocols
-
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): Providing encryption and digital signatures for emails, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of messages.
-
TLS (Transport Layer Security): Securing email traffic between mail servers, preventing eavesdropping and message tampering during transmission.
9. Use Email Security Tools
Finally, leveraging email security solutions can provide comprehensive protection against threats. These tools can include spam filters, antivirus software, email security software and advanced threat detection systems, each designed to target specific risks.
Recommended tools
-
Spam Filters: Block unwanted and potentially harmful emails from your inbox.
-
Antivirus and Anti-malware: Scan incoming emails for malware and prevent harmful software from being installed on your device.
-
Advanced Threat Protection (ATP): Detect and mitigate more sophisticated threats like ransomware or spear-phishing attacks.
Incorporating these tools into your comprehensive email security strategy ensures that your email system is safeguarded from various types of cyber threats.
How Can Aztech Help You?
Aztech offers a range of email security solutions tailored to meet your business's specific needs.
From employee training programmes to deploying advanced security tools, Aztech ensures your emails are secure and protected against cyber threats.
Our experts can help you implement the best practices outlined in this guide and provide ongoing support to keep your email system safe.
Conclusion
Protecting your email accounts from evolving cyber threats requires a proactive approach to email security best practices.
From training employees to use strong passwords and two-factor authentication, encrypting emails, and avoiding public Wi-Fi, these measures help mitigate the risk of data breaches, phishing schemes, and malicious email messages.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is email security important?
Email is a common target for hackers seeking access to personal and financial information, making strong email security measures essential.
2. How do I create strong passwords for my email account?
You must use a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Also, you should avoid using easily guessable information rather consider using a password manager.
3. How can I recognise phishing emails?
You should look out for malicious links, email attachments, and unsolicited messages that attempt to trick you into revealing personal or sensitive data.
4. Should I use encryption for all emails?
While it’s not necessary for every email, encrypting sensitive information and attachments is crucial for protecting email communications.
5. What are the email security protocols?
Security protocols like Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) protect emails from being altered or intercepted during transmission.
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)





